本文共 12325 字,大约阅读时间需要 41 分钟。
目录
【树结构】
数组下标查找数据速度很快,但插入数据需要拷贝数组,数组扩容,数据全体向后移动,所以插入数据效率低下。
链表在插入方面表现优良,但查找数据仍要遍历这个链表,查找效率低下。
哈希表(散列表)hash表其实是结合了数组和链表的优点,进行的折中方案。平衡了数组和链表的优缺点。但其存在哈希关键值的冲突(两个以上数据经过哈希运算得到了同一个哈希值),此时要采取方案,如:数组+链表 的形式处理冲突。且哈希表数组长度固定,若改变数组长度将导致所有已加入的数据,重新进行哈希运算。
树的结构,可以提高数据的存储,读取效率,在保证数据的检索速度时,也能保证数据的插入,删除,修改的速度
树的分类:
二叉排序树(BST),平衡二叉树(AVL树),红黑树,B-树(B树),B+树等
【二叉树基础】
概念:
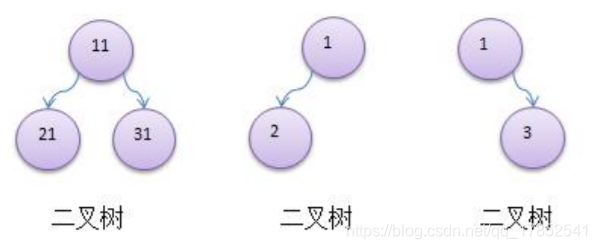
如果二叉树的所有叶子结点都在最后一层,并且结点总数=2^n-1,n为层数,该二叉树称之为满二叉树
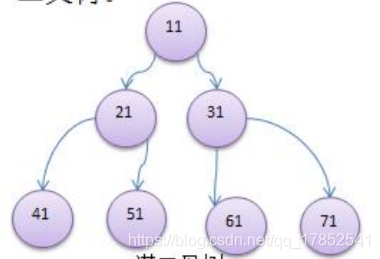
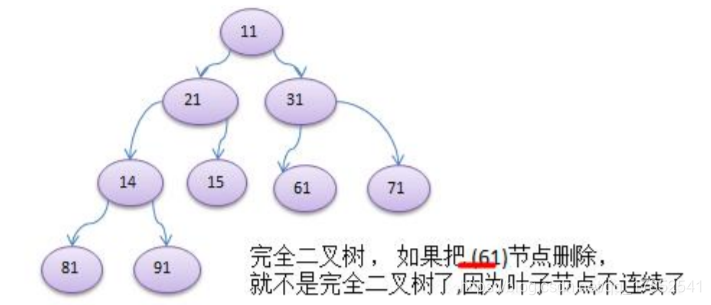
如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,称为完全二叉树
简易二叉树
1,创建二叉树:
没什么难度,只不过是Node结点类里next变为了left,right。
2,二叉树遍历:
前序遍历:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
小结:看输出父节点的顺序,就确定是前序,中序还是后序
代码实现:
package cn.dataStructureAndAlgorithm.demo.tree;class Node{ private int id; private String data; private Node left; private Node right; public Node(int id, String data) { this.id = id; this.data = data; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getData() { return data; } public void setData(String data) { this.data = data; } public Node getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(Node left) { this.left = left; } public Node getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(Node right) { this.right = right; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "id=" + id + ", data='" + data + '\'' + '}'; } //前序遍历 public void preOrder(){ System.out.println(this); if (this.left!=null){ this.left.preOrder(); } if (this.right!=null){ this.right.preOrder(); } } //中序遍历 public void infixOrder(){ if (this.left!=null){ this.left.infixOrder(); } System.out.println(this); if (this.right!=null){ this.right.infixOrder(); } } //后序遍历 public void postOrder(){ if (this.left!=null){ this.left.postOrder(); } if (this.right!=null){ this.right.postOrder(); } System.out.println(this); }}class BinaryTree{ private Node root;//根节点 public void setRoot(Node node){ this.root=node; } public Node getRoot() { return root; } //前序遍历 public void preOrder(){ if (this.root!=null){ this.root.preOrder(); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } } //中序遍历 public void infixOrder(){ if (this.root!=null){ this.root.infixOrder(); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } } //后序遍历 public void postOrder(){ if (this.root!=null){ this.root.postOrder(); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } }}public class 二叉树_BinaryTree { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建二叉树 BinaryTree binaryTree=new BinaryTree(); Node node1=new Node(1,"one"); Node node2=new Node(2,"two"); Node node3=new Node(3,"three"); Node node4=new Node(4,"four"); Node node5=new Node(5,"five"); binaryTree.setRoot(node1); binaryTree.getRoot().setLeft(node2); binaryTree.getRoot().setRight(node3); node3.setLeft(node4); node3.setRight(node5); System.out.println("前序遍历"); binaryTree.preOrder();//1,2,3,4,5 System.out.println("中序遍历"); binaryTree.infixOrder();//2,1,3,4,5 System.out.println("后序遍历"); binaryTree.postOrder();//2,3,4,5,1 }} 前序遍历Node{id=1, data='one'}Node{id=2, data='two'}Node{id=3, data='three'}Node{id=5, data='five'}Node{id=4, data='four'}中序遍历Node{id=2, data='two'}Node{id=1, data='one'}Node{id=5, data='five'}Node{id=3, data='three'}Node{id=4, data='four'}后序遍历Node{id=2, data='two'}Node{id=5, data='five'}Node{id=4, data='four'}Node{id=3, data='three'}Node{id=1, data='one'} 3,二叉树遍历查找:
就是在原有前中后遍历中,加入对id相等的判定即可。当判定相等时返回该节点。
代码实现:
Node类中新增
//前序查找 public Node preOrderSearch(int id){ if (this.getId()==id){ return this; } Node resNode=null; if (this.left!=null){ resNode=this.left.preOrderSearch(id); } if (resNode!=null){ return resNode; } if (this.right!=null){ resNode=this.right.preOrderSearch(id); } return resNode; } //中序查找 public Node infixOrderSearch(int id){ Node resNode=null; if (this.left!=null){ resNode=this.left.infixOrderSearch(id); } if (resNode!=null){ return resNode; } if (this.getId()==id){ return this; } if (this.right!=null){ resNode=this.right.infixOrderSearch(id); } return resNode; } //后序查找 public Node postOrderSearch(int id){ Node resNode=null; if (this.left!=null){ resNode=this.left.postOrderSearch(id); } if (resNode!=null){ return resNode; } if (this.right!=null){ resNode=this.right.postOrderSearch(id); } if (resNode!=null){ return resNode; } if (this.getId()==id){ return this; } return resNode; } binaryTree类中新增:
public void preOrderSearch(int id){ if (this.root!=null){ System.out.println("查询结果:"+this.root.preOrderSearch(id)); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } } //中序查找 public void infixOrderSearch(int id){ if (this.root!=null){ System.out.println("查询结果:"+this.root.infixOrderSearch(id)); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } } //前序查找 public void postOrderSearch(int id){ if (this.root!=null){ System.out.println("查询结果:"+this.root.postOrderSearch(id)); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } } 测试类中新增:
System.out.println("前序查找"); binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5); System.out.println("中序查找"); binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(1); System.out.println("后序查找"); binaryTree.postOrderSearch(0); 前序查找查询结果:Node{id=5, data='five'}中序查找查询结果:Node{id=1, data='one'}后序查找查询结果:null 4,二叉树简单结点删除:
这里实现的简单删除是指:删除根节点,相当于重置二叉树;删除叶子结点,即将叶子结点置空;删除非叶子结点,即将该结点之下的所有结点都一并删除
代码实现:
Node类新增:
//简单删除 public void delete(int id){ if (this.left!=null && this.left.getId()==id){//删除左子节点 this.left=null; return; } if (this.right!=null && this.right.getId()==id){//删除右子节点 this.right=null; return; } if (this.left!=null){//向左子树递归 this.left.delete(id); } if (this.right!=null){//向右子树递归 this.right.delete(id); } } binaryTree类新增:
//简单删除 public void delete(int id){ if (this.root!=null){ if (this.root.getId()==id){//删除根节点 this.root=null; }else{ this.root.delete(id); } }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空"); } } 测试类新增:
System.out.println("简单删除"); binaryTree.delete(3); binaryTree.preOrder(); 简单删除Node{id=1, data='one'}Node{id=2, data='two'}
顺序存储二叉树
二叉树中的内容可以通过顺序存储或链式存储进行储存。
顺序存储指的是使用顺序表(数组)存储二叉树。需要注意的是,顺序存储只适用于完全二叉树。换句话说,只有完全二叉树才可以使用顺序表存储。因此,如果我们想顺序存储普通二叉树,需要提前将普通二叉树转化为完全二叉树。
顺序(数组)存储二叉树需要遵循一定规律:
树对应数组索引从root结点开始从左向右由0到n;n索引结点左节点对应数组索引为2*n+1;右结点对应数组索引为2*n+2;对应父节点为 (n-1)/2

遵循以上规律,我们只需要在前中后序遍历中按照规律,就可以实现数组的前中后序遍历。
代码实现:
package cn.dataStructureAndAlgorithm.demo.tree;class ArrBinaryTree{ private int arr[]; public ArrBinaryTree(int[] arr) { this.arr = arr; } //前序遍历 public void preOrder(){ preOrder(0); } public void preOrder(int index){ if (arr.length==0 || arr==null){//空数组不遍历 System.out.println("空数组"); return; } System.out.print(arr[index]+" "); //左遍历 if ((index*2+1) 前序遍历1 2 4 5 3 6 7 中序遍历4 2 5 1 6 3 7 后序遍历4 5 2 6 7 3 1
线索化二叉树
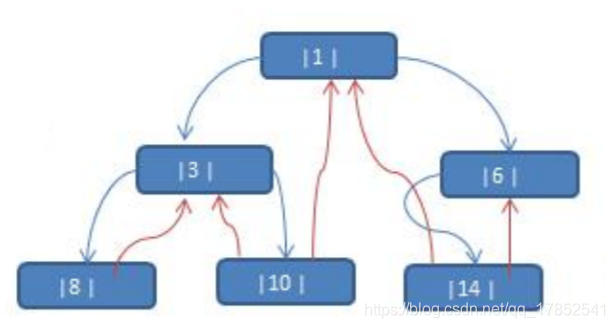
所谓线索化二叉树就是将二叉树中存在空指针域的结点,将其左指针指向其前一个结点(前驱结点:即遍历后其排序之前的结点),将其右指针指向其后一个结点(后继结点:即遍历后其排序之后的结点)
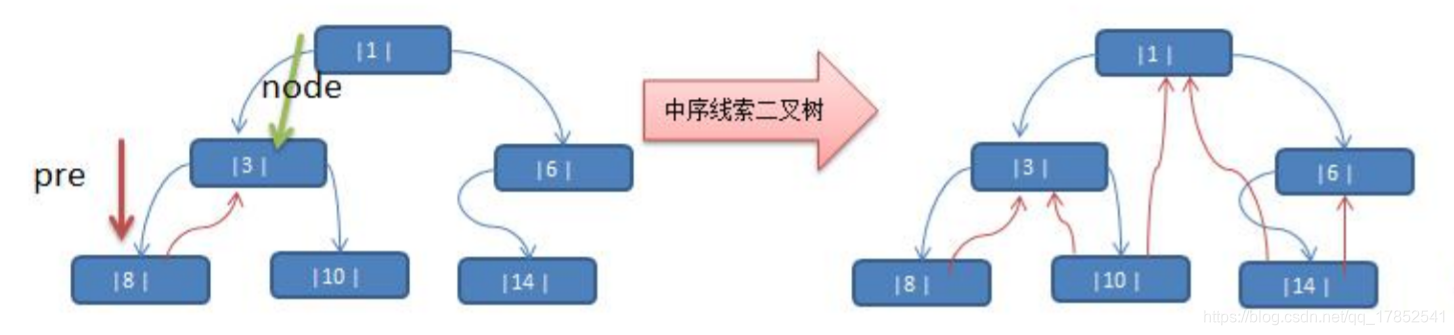
上图中中序遍历后为{8,3,10,1,14,6},所以8的左指针指向null,右指针指向3。以此类推
算法分析:(以中序遍历线索化为例)
采用递归的形式进行线索化,需要一个pre用于保存前驱结点,而node保存当前结点。
遍历过程中,当发现结点的左子节点为空时就进行前驱结点的链接。当发现右子节点为空时,这个不好进行线索化。因为没有指向后继结点的指针。所以要先让其递归一次,使得原先的pre指向node,原先的node指向后继结点。这样后再对pre的右节点进行线索化,连接至node即可完成(开始理解起来有点难!)
代码实现:
package cn.dataStructureAndAlgorithm.demo.tree;class Node_TB { private int id; private String data; private Node_TB left; private Node_TB right; //Type=0说明保存的为正常结点,1为前驱或后继结点 private int leftType; private int rightType; public void setLeftType(int leftType) { this.leftType = leftType; } public void setRightType(int rightType) { this.rightType = rightType; } public Node_TB(int id, String data) { this.id = id; this.data = data; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getData() { return data; } public void setData(String data) { this.data = data; } public Node_TB getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(Node_TB left) { this.left = left; } public Node_TB getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(Node_TB right) { this.right = right; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "id=" + id + ", data='" + data + '\'' + '}'; }}class ThreadBinaryTree{ private Node_TB root;//根节点 private Node_TB pre=null;//上一个结点 public void setRoot(Node_TB node){ this.root=node; } public Node_TB getRoot() { return root; } //递归方法:中序线索化二叉树 public void threadTree(Node_TB node){ if (node==null){//递归结束条件:空节点不能线索化 return; } //线索化左子树 threadTree(node.getLeft()); //线索化当前结点 //1,线索化左结点 pre保存前上一个结点,node为当前结点,当node的left空时将left连接到pre上即可 if (node.getLeft()==null){ node.setLeft(pre);//链接到前驱结点 node.setLeftType(1); } //2,线索化右节点 【有点难】 判断完左子树后,由于pre的right一定不为空,所以会逃过下面的判断进行一次递归后又来到这 //此时pre保存上一次的node,而node保存的是上一次node的后继结点,此时pre的right为空,满足条件进行线索化 if (pre!=null && pre.getRight()==null){ pre.setRight(node); pre.setRightType(1); } pre=node;//pre指向后移 //线索化右子树 threadTree(node.getRight()); }}public class 线索化二叉树_ThreadBinaryTree { public static void main(String[] args) { Node_TB node1=new Node_TB(1,"one"); Node_TB node2=new Node_TB(2,"two"); Node_TB node3=new Node_TB(3,"three"); Node_TB node4=new Node_TB(4,"four"); Node_TB node5=new Node_TB(5,"five"); Node_TB node6=new Node_TB(6,"six"); Node_TB node7=new Node_TB(7,"seven"); ThreadBinaryTree threadBinaryTree=new ThreadBinaryTree(); threadBinaryTree.setRoot(node1); node1.setLeft(node2); node1.setRight(node3); node2.setLeft(node4); node2.setRight(node5); node3.setLeft(node6); node3.setRight(node7); threadBinaryTree.threadTree(node1); System.out.println(node4.getRight()); }} Node{id=2, data='two'} 线索化二叉树的遍历:
二叉树被线索化后,其叶子节点,没有了空指针域。用传统遍历时,会导致找不到结束递归的条件。造成死龟,引发栈溢出。所以要重新结合线索化二叉树的特点,重新设计。
代码实现:
ThreadBinaryTree类新增方法:
//中序遍历的线索化二叉树遍历(非递归) public void ThreadTreeList() { Node_TB node = this.root; //循环遍历到结尾 while (node != null) { //1,遍历左子树阶段 //循环直到找到left类型为1时,它一定是中序遍历的左结点数据,将其输出 while (node.getLeftType() == 0) { node = node.getLeft(); } System.out.println(node); //2,遍历中间阶段(由于树已被中序线索化,所以遍历right,就是在找中间的那个值阶段) //循环看right类型是否为1,是1声明它一定是后继结点,可以输出 while (node.getRightType() == 1) { node = node.getRight(); System.out.println(node); } //3,遍历右子树阶段 node = node.getRight(); } } 这个方法原理需要deBug一下才能明白。
测试类新增:
threadBinaryTree.ThreadTreeList();
结果输出:
Node{id=2, data='two'}Node{id=4, data='four'}Node{id=2, data='two'}Node{id=5, data='five'}Node{id=1, data='one'}Node{id=6, data='six'}Node{id=3, data='three'}Node{id=7, data='seven'} 以上遍历是基于中序线索化二叉树实现的。其实还可以实现前序线索化,后序线索化。在这里先挖个坑~
有关树结构的其他内容,见下各链接
<-- 宝藏在此(doge)
转载地址:http://jcztz.baihongyu.com/